La normalización, el canal UNE hacia la economía circular
• La Asociación Española de Normalización, UNE, ha publicado un informe que contiene más de 300 normas UNE que han sido aportadas por cerca de 50 Comités técnicos de la entidad para impulsar la economía circular.
El documento de UNE, Estudio de la contribución de las normas técnicas a la economía circular, describe el papel de las normas UNE como elementos facilitadores para la transición a la economía circular de empresas y entidades de distinta naturaleza.
Los estándares recogidos incluyen requisitos para el uso de los residuos en los procesos de producción, metodologías para determinar las sustancias peligrosas que puedan dificultar la implementación de medidas circulares o para evaluar la durabilidad, reparabilidad, reciclabilidad o biodegradabilidad de multitud de productos, entre otros muchos aspectos.
El informe, que abarca numerosos sectores (industria, turismo, moda, salud o construcción, entre otros), va dirigido tanto a empresas como a reguladores que buscan referencias para determinar la economía circular en el mercado.
El Instituto Tecnológico AIDIMME colabora estrechamente en UNE, es miembro de su Junta Directiva, coordina varias secretarías de comités de normalización y participa en numerosos subcomités y grupos de trabajo, dentro de una extensa política y cultura de la normalización en el ámbito nacional e internacional.
Concretamente, sobre las normas relacionadas con la materia específica de la economía circular que abarca el estudio, AIDIMME participa en los siguientes Comités Técnicos de Normalización, CTN, de los 33 comités de normalización, 6 secretarías técnicas y la coordinación de 4 grupos de trabajo en los que está integrado:
- CTN 11 Mobiliario (Gestión de la Secretaría)
- CTN 38 Metales Ligeros y sus aleaciones (Vocalía)
- CTN 49 Envases y embalajes. Aspectos horizontales y de gestión medioambiental (Vocalía)
- CTN 89 Mobiliario de oficina (Vocalía)
- CTN 85 Cerramiento de huecos en la edificación y sus accesorios (Vocalía)
- CTN 112 Corrosión y Protección de los Materiales Metálicos (Gestión de la Secretaría)
- CTN 143 Adhesivos y sellantes (Vocalía)
- CTN 150 Gestión Ambiental (Vocalía)
- CTN 178 Ciudades inteligentes (Vocalía)
- CTN 205 Lámparas y equipos asociados (Vocalía)
- CTN 323 Economía circular

Asimismo, establecen un marco de actuación común para definir los principios y las técnicas aplicables en economía circular y evitar el «greenwashing«, ya que según un informe de la Comisión Europea publicado el año pasado, el 42% de las empresas de la UE que se anuncian en internet con publicidad sostenible caen en esta mala práctica.
Actualmente, UNE, en colaboración con los organismos internacionales de normalización, está trabajando en estándares globales dirigidos a establecer modelos de negocios circulares y a medir su circularidad en diferentes niveles -producto, servicio y actividad de la organización-.
Para más información contacte con AIDIMME.
Visitas: [wpstatistics stat=pagevisits time=total id=29004]
Interview with José Luis Sánchez, head of industrial development at AIDIMME
Information published by Javier García for Interempresas
José Luis Sánchez is head of industrial development at AIDIMME, a division that works to improve the manufacturing process efficiency, especially in the wood-furniture and metalworking sectors. In order to do so, the division uses traditional process-improvement tools in a consultancy format (process analysis, lean manufacturing-based techniques, developing improvement methods, customised training, etc.) or technologies focused on digitalisation processes, such as monitoring, automation, robotics, artificial vision, etc. The division is also part of the Plasma project, a demonstrator for 4.0 technologies that captures reliable data within two weeks to start the design of the scanning processes for smart or automated manufacturing. José Luis Sánchez explains what the digitalisation designing entails and how it can help a company, especially a SME.

AIDIMME has initiated the Plasma system. What does it entail?
The Plasma project began in 2018 with the help of IVACE. It focuses on demonstrating the possibilities the digitalisation of these technologies offers in the manufacturing industry, especially in our reference field. Plasma has three demonstrators, two of them are portable and can be moved to the interested companies and the other is installed at AIDIMME – it reproduces a functional manufacturing line for personalised products.
What technologies does it incorporate?
One of the portable demonstrators has a complete process-monitoring system that can extract the information of any manufacturing process and show its operating status – to measure efficiency or analyse any relationship between variables that may interest the company. For example, it can measure product quality and relate it to the relevant variables in the process.
Another demonstrator is a collaborative robot installed over a mobile platform. It can be transferred to a company to evaluate the viability of the automation of any process. For example, it has been used to evaluate automatic machine loading and unloading, sanding and polishing procedures, piece unloading in transport systems, piece assembly, etc. The production line combines multiple technologies.
Which technologies?
RFID identification, collaborative automation focused on assembling parts in cooperation with a person, augmented reality for staff training, machine control integration in the production control system via OPC UA, additive manufacturing for the serial part production…
What type and profile of companies is it aimed at? Who can benefit from the advantages?
Plasma is at the disposal of any company interested in evaluating the integration of these technologies in their processes. There is no company-defined profile for using a demonstrator, though, compared to large companies, normally small and medium-sized enterprises have fewer possibilities to try this type of technology.
Which sectors does it focus on?
Originally it is aimed at the metalworking and wood-furniture sectors, although some technologies can be applied to any manufacturing sector.

There has been talk of mass customisation. What can this platform do to this effect?
As I mentioned, the Plasma production line is designed to manufacture products that are completely personalised, so the implemented technologies are geared in this direction. For example, the fact that each manufactured product is identified individually allows the product itself to communicate directly with each process, automatically indicating the next operation that must take place. This enables the complete automation of the production flow, regardless of the lot size. Each product unit can be different from the previous and the next since the identifier will tell the machine what to do when it has reached a certain procedure.
This entails the machines to be able to adjust automatically and rapidly…
Yes, and by doing so a hundred equal units or a hundred different ones can be manufactured. And if in the assembly process there is a completely flexible machine – like a collaborative robot, a computerised quality-control system based on artificial vision – and is all complemented with an augmented reality system which indicates the specific packaging operation sequence it must carry out for each product. A completely flexible and adequate process is provided for personalised manufacturing or to produce larger or smaller batches (depending on the demand).
It is said that the system allows to evaluate the viability of a digital transformation process and to quantify the investment needed. How does it do it? What aspects does it consider?
Both mobile demonstrators can evaluate the viability of the technologies involved. Because they can be assembled directly into any process, they allow the own company to evaluate the advantages in the monitoring of the processes and the automation of some procedures.
What is this report about?
It analyses the gathered information in monitoring, or the cycle times achieved in the automation. From this data and the estimated investment or expenditures needed to implement the technologies, a payback period can be estimated. Therefore, these companies are provided with valuable information for the decision-making. The tests have not always acquired returns on investment that advise the implementation of one technology or the other.
How is this system being received?
At the beginning many demonstrations took place and the teams were nearly saturated, but now we are available to use the demonstrators in those companies interested in evaluating the digitalisation benefits, with a short waiting time.

Sometimes it seems that in exhibitions and conferences, the solutions for the Industry 4.0 are presented and talked about, though the market is still not assimilating them. In other words, the supply and the demand are moving in different directions, and automation suppliers develop products and solutions that are not yet a reality in companies and production facilities in our country. How aware do you think the industrial sector is – especially the SME – about the new technologies?
I believe the industry is aware of the importance in digitalisation and knows many of the technologies that are currently available and which they can benefit from. But the solution developers’ pace and the industry’s pace are very different, due to the nature of each activity.
In the technological world, anyone who does not bring out an innovation every few months seems to be left behind. But the industry cannot modify constantly its methods, technologies or processes, because the clients demand stability and continuity. The changes must be carefully made and must not disrupt the essence of the business.
This does not mean that the industry cannot integrate the advances that are taking place in each field, but the path must be explored step by step, knowing the strategic priorities. I think this is still one of the main problems, because there are still many companies that do not question their priorities, even if we witness the constant change our surrounding is experiencing.
What arguments would you use to convince the industry about the advantages of the Plasma system?
The best way of convincing is by demonstrating in a practical way that a proposal – or in this case a technology – can work. On this basis, I invite them to experiment and, in view of the results, reach their own decision.
Access the Interempresas interview through this link.
Views: [wpstatistics stat=pagevisits time=total id=30574]
INEX-ADAM, the European Project Working to Expand Additive Manufacturing Knowledge
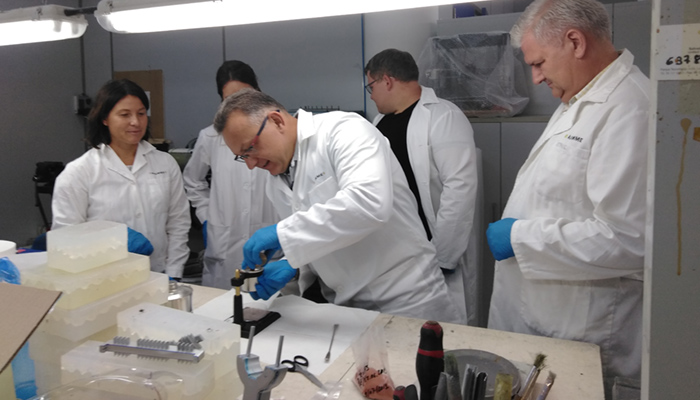
One of the main barriers that companies face when adopting additive manufacturing in their activity is lack of training or knowledge of materials. To address this situation, different types of training and projects are emerging with the aim of democratizing the use of 3D printing and facilitating its integration as a complementary production technology. One of these projects is the European INEX-ADAM, which arose with the goal of facilitating access to knowledge of additive manufacturing run by the University of Zagreb in the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture (UNIZAG FSB). Several institutions from different European countries have participated in it, among them, the technological center AIDIMME. We talked to Olga Jordá, R&D engineer at AIDIMME, to learn more about this interesting initiative that promotes the adoption of 3D printing in Europe.
3DN: Can you briefly introduce yourself and explain what the INEX-ADAM project is?
I am Olga Jordá, Industrial Engineer by the Polytechnic University of Valencia since 2001. I have been an R&D Engineer in the field of New Manufacturing Processes at AIDIMME since 2002, I am a specialist in additive manufacturing technologies, mainly in the development of new industrial applications, the development of training plans for knowledge transfer, and in the validation of additive manufacturing processes.
The INEX-ADAM project (INcreasing EXcellence on ADvanced Additive Manufacturing) is a European Twinning call project that started in 2018 and just ended in February 2022. The main objective is to facilitate and equip the Center for Additive Technologies, CATeh at the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture in Zagreb, Croatia, to become an industry reference center by increasing excellence and innovative capacity for research in the field of additive manufacturing.
3DN: Which European organizations are involved and what has each been responsible for?
The consortium has been formed with the objective of creating a Network of Advanced Manufacturing Expert Centers. To this end, the partners have contributed their knowledge in additive manufacturing (AM) technologies and applications to increase the competences at UNIZA
G FSB. In addition to AIDIMME, several European universities are involved in the project. Lund University in Sweden has focused on design for additive manufacturing (DfAM), selection of materials and technologies according to each type of application. The Austrian University of Mining, Metallurgy and Materials has focused on the development and processing of thermoplastic materials for FFF additive technology, as well as the characterization of materials and how to link material properties with the process. Brunel University London in England has focused its training on the state of the art of additive manufacturing, knowledge of current regulations, material modeling techniques, the innovation cooperation process and business models.

It should be noted that before starting the training period, visits were made to all partners in order to know their competences and skills, as well as the facilities of each of them, so it was easier to distribute the different topics for the training of UNIZAG FSB staff participating in the project. In addition, after the training period, all project partners participated in several workshops and summer schools specific to the design process adapted to additive manufacturing and the use of additive manufacturing in the industrial and healthcare sectors. Given the current situation, most of the workshops and conferences have been held virtually.
3DN: Specifically, what is the role of AIDIMME within this project?
AIDIMME’s participation in the INEX-ADAM project has focused on sharing its knowledge in different topics, through theoretical and practical sessions. More specifically, we have promoted knowledge on the use of metallic materials as raw material, powder bed fusion technologies, both in metal and polymer, the complete workflow of additive manufacturing, the validation of parts and the entire manufacturing process, and much more. In addition to the training, AIDIMME has participated in all the conferences, workshops and summer schools showing its knowledge in the above topics.

3DN: What is the ADAM platform and how important is it for users? What other broadcast formats do you work with?
The idea of the advanced additive manufacturing platform (ADAM platform) is to become a meeting point for intensive cooperation. The project partners will support the platform members in advanced AF applications or in the preparation of training materials. ADAM will offer opportunities for knowledge transfer, R&D, promotion, networking, industrial application and innovation for industry professionals. Experts from partner institutions are highly trained and well equipped with a wide range of AF equipment that can help to successfully solve any challenge. It is possible to apply for registration on the platform by following this link or by contacting the person in charge of platform maintenance.
In addition to the ADAM platform, the entire project consortium has participated in the elaboration of the book “A Guide to Additive Manufacturing” which is in the process of publication. In the coming months it will be available in Springer Nature in the Springer Tracts in Additive Manufacturing series and will be freely accessible to all those interested in Additive Manufacturing.

3DN: Why is it important that projects like INEX-ADAM continue to be implemented in the European framework?
Cooperation between different partners across Europe is a strength and a great enrichment for all, not only individually but also as a whole. In these difficult times, the union and collaboration between entities across Europe, the establishment of common lines of research and knowledge transfer, are the key to strengthening the European industry.
3DN: Any last words for our readers?
This type of European projects where there is collaboration and cooperation between entities throughout Europe are of great importance since knowledge and opinions are shared and the state of evolution of a given technology in the different countries is known first hand. Three years of collaboration in the project generates an atmosphere of trust and collaboration that enriches all project participants. In addition, this project focused on knowledge transfer has revealed the importance and the need for formal training in this area in general in all project partner countries that can be extended to Europe. You can find more information about the project HERE.
You can access the full publication through this link.
Project Number: 21700189
Grant Agreement: 810708
Duration: From 01/07/2018 to 28/02/2022
Coordinated in AIDIMME by: JORDA FERRANDO, OLGA
R&D Line: ADDITIVE MANUFACTURE
For more information contact AIDIMME.
Visitors: [wpstatistics stat=pagevisits time=total id=27917]
INEX-ADAM, el proyecto que amplia el conocimiento sobre la fabricación aditiva
Una de las principales barreras con las que se encuentran las empresas a la hora de adoptar la fabricación aditiva en su actividad es la falta de formación o conocimiento en esta material. Para hacer frente a esta situación, están surgiendo diferentes tipos de formaciones y proyectos con el objetivo de democratizar la utilización de la impresión 3D y facilitar su integración como tecnología de producción complementaria. Uno de estos proyectos es el europeo INEX-ADAM, que surge con la idea de facilitar el acceso al conocimiento de la fabricación aditiva por parte de la Facultad de Ingeniería Mecánica y Arquitectura Naval de Zagreb. En él han participado varias instituciones de diferentes países europeos, entre ellos, el centro tecnológico AIDIMME. Hemos hablado con Olga Jordá, ingeniera de I+D en AIDIMME, para conocer más a cerca de esta interesante iniciativa que fomenta la adopción de la impresión 3D en Europa.
3DN: ¿Puedes presentarte brevemente y explicar qué es el proyecto INEX-ADAM?
Soy Olga Jordá, Ingeniera Industrial por la Universidad Politécnica de Valencia desde el 2001. Ingeniera de I+D en el área de Nuevos procesos de fabricación de AIDIMME desde 2002, especialista en las tecnologías de fabricación aditiva, principalmente en el desarrollo de nuevas aplicaciones industriales, el desarrollo de planes de formación para transferencia de conocimiento, y en la validación de los procesos de fabricación aditiva.
El proyecto INEX-ADAM (INcreasing EXcellence on ADvanced Additive Manufacturing) es un proyecto europeo de la convocatoria Twinning que empezó en el 2018 y acaba de terminar en febrero del 2022. El objetivo principal es facilitar y dotar de conocimientos al Centro de Tecnologías Aditivas, CATeh de la Facultad de Ingeniería Mecánica y Arquitectura Naval de Zagreb, Croacia, para que se convierta en un centro de referencia sectorial mediante el aumento de la excelencia y capacidad innovadora para la investigación en el campo de la fabricación aditiva.
3DN: ¿Qué organizaciones europeas están involucradas y de qué se ha encargado cada una?
El consorcio ha sido formado con el objetivo de crear una Red de Centros Expertos en Fabricación Avanzada. Para ello, los socios han aportado su conocimiento en tecnologías y aplicaciones de la fabricación aditiva (FA) para incrementar las competencias de UNIZAG FSB. Además de AIDIMME, en el proyecto intervienen varias universidades europeas. La Universidad Lund de Suecia se ha centrado en el diseño para fabricación aditiva (DfAM), selección de los materiales y tecnologías según cada tipo de aplicación. La Universidad de Minería, Metalurgia y Materiales de Austria, se ha centrado en el desarrollo y procesado de materiales termoplásticos para la tecnología aditiva FFF, así como la caracterización de los materiales y como enlazar las propiedades del material con el proceso. La Universidad Brunel de Inglaterra ha centrado su formación en el estado del arte de la fabricación aditiva, en el conocimiento de la normativa actual, las técnicas de modelado de materiales, el proceso de cooperación en innovación y los modelos de negocio.

Cabe destacar que antes de iniciar el periodo de formación se realizaron visitas a todos los socios con el fin de conocer sus competencias y habilidades, así como las instalaciones de cada uno de ellos, de este modo fue mas sencillo la distribución de los diferentes temas para la formación del personal de UNIZAG FSB participante en el proyecto. Además, tras el periodo de formación, todos los socios del proyecto, han participado en varios talleres y escuelas de verano específicos para el proceso de diseño adaptado a fabricación aditiva y el uso de la fabricación aditiva en el sector industrial y en el sector sanitario. Dada la situación actual la mayoría de los talleres y conferencia se han realizado de forma virtual.
3DN: En concreto, ¿cuál es la función de AIDIMME dentro de este proyecto?
La participación de AIDIMME en el proyecto INEX-ADAM se ha centrado en compartir su conocimiento en diferentes temáticas, mediante sesiones teóricas y prácticas. En concreto hemos fomentado el conocimiento en cuanto al uso de materiales metálicos como materia prima, tecnologías de fusión por lecho de polvo, tanto en metal como en polímero, el workflow completo de la fabricación aditiva, la validación de piezas y de todo el proceso de fabricación, y mucho más. Además de la formación, AIDIMME ha participado en todas las conferencias, workshops y escuelas de verano mostrando su conocimiento en las temáticas anteriores.

3DN: ¿En qué campos de aplicación destaca AIDIMME en fabricación aditiva?¿Por qué es interesante para las empresas españolas?
AIDIMME es un Instituto Tecnológico de referencia que cuenta con más de 30 años de experiencia en diferentes sectores de aplicación, contribuyendo a incrementar la competitividad de las empresas en los mercados nacionales e internacionales. La Unidad de Nuevos Procesos de fabricación (NPF) de AIDIMME aplica la innovación en los procesos, principalmente, en aquellos apoyados en la aplicación de tecnologías de fabricación aditiva. Con esta Unidad se persigue que la impresión 3D se convierta en un vector de competitividad para las empresas, a través de diferentes servicios.
AIDIMME tiene una elevada experiencia en las tecnologías de Fabricación Aditiva desde el 1997 donde incorporó su primera máquina de fabricación aditiva que procesaba resina. En los últimos años el departamento de Nuevos Procesos de Fabricación ha crecido notablemente disponiendo de 13 tecnologías de fabricación aditiva que procesan un gran numero de materiales metálicos, así como poliméricos. En la actualidad, AIDMME es considerado como uno de los centros tecnológicos más relevantes en la materia con un alto compromiso de transferencia y colaboración con la industria. Cientos de empresas han confiado en nosotros para la adopción de estas novedosas tecnologías de fabricación.
3DN: ¿Qué es la plataforma ADAM y cuál es su importancia para los usuarios? ¿Con qué otros formatos de difusión trabajáis?
La idea de la plataforma de fabricación aditiva avanzada (plataforma ADAM) es convertirse en un punto de encuentro para la cooperación intensiva. Los socios del proyecto apoyarán a los miembros de la plataforma en aplicaciones de la FA avanzada o en la preparación de materiales didácticos. ADAM ofrecerá oportunidades para la transferencia de conocimiento, I+D, promoción, creación de redes, aplicación industrial e innovación para profesionales de la industria. Los expertos de las instituciones socias están altamente capacitados y bien equipados con una amplia gama de equipos de FA que pueden ayudar a resolver con éxito cualquier desafío. Es posible solicitar el registro en la plataforma en este enlace o bien contactando con la persona encargada del mantenimiento de la plataforma.
Además de la plataforma ADAM, todo el consorcio del proyecto hemos participado en la elaboración del libro “A Guide to Additive Manufacturing” que esta en proceso de publicación. En los próximos meses estará disponible en Springer Nature en la serie Springer Tracts in Additive Manufacturing y será de acceso libre para todas aquellas personas interesadas en la Fabricación Aditiva.

3DN: ¿Por qué es importante que proyectos como INEX-ADAM se sigan implementando en el marco europeo?
La cooperación entre diferentes socios a lo largo de Europa implica una fortaleza y un gran enriquecimiento para todos, no solo de forma particular sino también como conjunto. En estos tiempos tan difíciles, la unión y colaboración entre entidades a lo largo de Europa, el establecimiento de unas líneas de investigación comunes y una transferencia de conocimiento, son la clave para fortalecer la industria Europea.
3DN: ¿Unas últimas palabras para nuestros lectores?
Este tipo de proyectos europeos donde hay una colaboración y cooperación entre entidades a lo largo de Europa son de gran importancia ya que se comparte conocimiento, opiniones y se conoce de primera mano el estado de la evolución de una determinada tecnología en los diferentes países. Tres años de colaboración en el proyecto hace que se genere un ambiente de confianza y colaboración que enriquece a todos los participantes del proyecto. Además, este proyecto centrado en la transferencia de conocimiento ha revelado la importancia y la necesidad de formación reglada en esta temática en general en todos los países socios del proyecto que puede hacerse extensivo a Europa. Puedes encontrar más información del proyecto aquí.
Puede acceder a la publicación completa a través de este enlace.
Número de proyecto: 21700189
Expediente: 810708
Duración: Del 01/07/2018 al 28/02/2022
Coordinado en AIDIMME por: JORDA FERRANDO,OLGA
Línea de I+D: FABRICACIÓN ADITIVA
Para más información contacte con AIDIMME.
Visitas: [wpstatistics stat=pagevisits time=total id=27901]

INEX-ADAM, the European Project Working to Expand Additive Manufacturing Knowledge
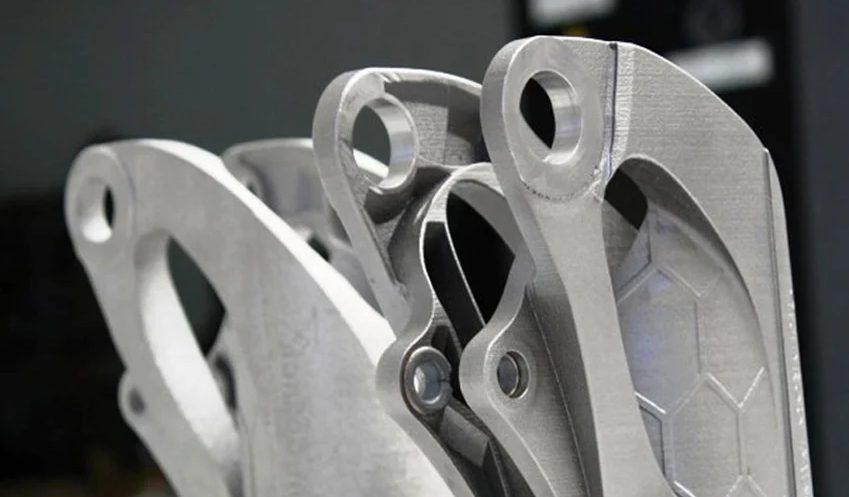
One of the main barriers that companies face when adopting additive manufacturing in their activity is lack of training or knowledge of materials. To address this situation, different types of training and projects are emerging with the aim of democratizing the use of 3D printing and facilitating its integration as a complementary production technology. One of these projects is the European INEX-ADAM, which arose with the goal of facilitating access to knowledge of additive manufacturing run by the University of Zagreb in the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture (UNIZAG FSB). Several institutions from different European countries have participated in it, among them, the technological center AIDIMME. We talked to Olga Jordá, R&D engineer at AIDIMME, to learn more about this interesting initiative that promotes the adoption of 3D printing in Europe.
3DN: Can you briefly introduce yourself and explain what the INEX-ADAM project is?
I am Olga Jordá, Industrial Engineer by the Polytechnic University of Valencia since 2001. I have been an R&D Engineer in the field of New Manufacturing Processes at AIDIMME since 2002, I am a specialist in additive manufacturing technologies, mainly in the development of new industrial applications, the development of training plans for knowledge transfer, and in the validation of additive manufacturing processes.
The INEX-ADAM project (INcreasing EXcellence on ADvanced Additive Manufacturing) is a European Twinning call project that started in 2018 and just ended in February 2022. The main objective is to facilitate and equip the Center for Additive Technologies, CATeh at the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture in Zagreb, Croatia, to become an industry reference center by increasing excellence and innovative capacity for research in the field of additive manufacturing.
3DN: Which European organizations are involved and what has each been responsible for?
The consortium has been formed with the objective of creating a Network of Advanced Manufacturing Expert Centers. To this end, the partners have contributed their knowledge in additive manufacturing (AM) technologies and applications to increase the competences at UNIZA
G FSB. In addition to AIDIMME, several European universities are involved in the project. Lund University in Sweden has focused on design for additive manufacturing (DfAM), selection of materials and technologies according to each type of application. The Austrian University of Mining, Metallurgy and Materials has focused on the development and processing of thermoplastic materials for FFF additive technology, as well as the characterization of materials and how to link material properties with the process. Brunel University London in England has focused its training on the state of the art of additive manufacturing, knowledge of current regulations, material modeling techniques, the innovation cooperation process and business models.

It should be noted that before starting the training period, visits were made to all partners in order to know their competences and skills, as well as the facilities of each of them, so it was easier to distribute the different topics for the training of UNIZAG FSB staff participating in the project. In addition, after the training period, all project partners participated in several workshops and summer schools specific to the design process adapted to additive manufacturing and the use of additive manufacturing in the industrial and healthcare sectors. Given the current situation, most of the workshops and conferences have been held virtually.
3DN: Specifically, what is the role of AIDIMME within this project?
AIDIMME’s participation in the INEX-ADAM project has focused on sharing its knowledge in different topics, through theoretical and practical sessions. More specifically, we have promoted knowledge on the use of metallic materials as raw material, powder bed fusion technologies, both in metal and polymer, the complete workflow of additive manufacturing, the validation of parts and the entire manufacturing process, and much more. In addition to the training, AIDIMME has participated in all the conferences, workshops and summer schools showing its knowledge in the above topics.

3DN: What is the ADAM platform and how important is it for users? What other broadcast formats do you work with?
The idea of the advanced additive manufacturing platform (ADAM platform) is to become a meeting point for intensive cooperation. The project partners will support the platform members in advanced AF applications or in the preparation of training materials. ADAM will offer opportunities for knowledge transfer, R&D, promotion, networking, industrial application and innovation for industry professionals. Experts from partner institutions are highly trained and well equipped with a wide range of AF equipment that can help to successfully solve any challenge. It is possible to apply for registration on the platform by following this link or by contacting the person in charge of platform maintenance.
In addition to the ADAM platform, the entire project consortium has participated in the elaboration of the book “A Guide to Additive Manufacturing” which is in the process of publication. In the coming months it will be available in Springer Nature in the Springer Tracts in Additive Manufacturing series and will be freely accessible to all those interested in Additive Manufacturing.

3DN: Why is it important that projects like INEX-ADAM continue to be implemented in the European framework?
Cooperation between different partners across Europe is a strength and a great enrichment for all, not only individually but also as a whole. In these difficult times, the union and collaboration between entities across Europe, the establishment of common lines of research and knowledge transfer, are the key to strengthening the European industry.
3DN: Any last words for our readers?
This type of European projects where there is collaboration and cooperation between entities throughout Europe are of great importance since knowledge and opinions are shared and the state of evolution of a given technology in the different countries is known first hand. Three years of collaboration in the project generates an atmosphere of trust and collaboration that enriches all project participants. In addition, this project focused on knowledge transfer has revealed the importance and the need for formal training in this area in general in all project partner countries that can be extended to Europe. You can find more information about the project HERE.
You can access the full publication through this link.
Project Number: 21700189
Grant Agreement: 810708
Duration: From 01/07/2018 to 28/02/2022
Coordinated in AIDIMME by: JORDA FERRANDO, OLGA
R&D Line: ADDITIVE MANUFACTURE
For more information contact AIDIMME.
Visitors: [wpstatistics stat=pagevisits time=total id=27901]
Nueva sesión de AVIA Sinergy con la colaboración de AIDIMME
La nueva sesión de AVIA Sinergy se celebrará el próximo 30 de marzo a las 16:00 horas y hasta las 17:00 horas. En esta ocasión se traslada hasta las instalaciones de AIDIMME, Instituto Tecnológico Metalmecánico, Mueble, Madera, Embalaje y Afines.
 La dirección es Avenida Benjamin Franklin, 13, del Parc Tecnològic de Paterna.
La dirección es Avenida Benjamin Franklin, 13, del Parc Tecnològic de Paterna.
Se trata de una oportunidad para establecer contactos empresariales y comerciales.
En el Link adjunto se encuentra el documento de inscripción:
Para más información contacte con AIDIMME.
Visitas: [wpstatistics stat=pagevisits time=total id=27557]
Convocatoria de participación de empresas del sector forestal, madera y mueble – Proyecto WoodMarkets (Interreg Sudoe)


Toda la información en este enlace: https://www.fondoseuropeos.eu/files/Convocatoria_WOODMARKETS_ES.pdf
Visitas: [wpstatistics stat=pagevisits time=total id=27686]
La madera de Rusia y Bielorrusia considerada «madera de conflicto» por PEFC durante al menos 6 meses
Toda la madera originaria de Rusia y Bielorrusia es «madera de conflicto» y, por tanto, no se puede utilizar en productos certificados PEFC, según ha aclarado la Junta Directiva de PEFC International.
PEFC está extremadamente preocupado por el ataque del gobierno ruso a Ucrania, según ha señalado la organización en un comunicado remitido ayer a los medios de comunicación.
La invasión militar está en oposición directa a nuestros valores fundamentales, indica la nota, que añade que «esta agresión causa dolor y muerte indescriptibles e inaceptables a personas inocentes, incluidas mujeres y niños.» También tiene un impacto destructivo inmediato y a largo plazo en el medio ambiente, en los bosques y en las muchas personas que dependen de los bosques para su sustento, precisa la información.
La aclaración de que la madera de Rusia y Bielorrusia es madera de conflicto es el resultado de la reunión extraordinaria de la Junta Directiva Internacional de PEFC, celebrada el pasado 4 de marzo, para discutir la agresión militar del Vladímir Putin contra Ucrania y sus implicaciones para PEFC y los propietarios y empresas forestales certificados por PEFC.
La categorización de la madera de Rusia y Bielorrusia como madera de conflicto se produce tras la adopción por la Asamblea General de las Naciones Unidas de la Resolución sobre la agresión contra Ucrania, que «condena en los términos más enérgicos la agresión de la Federación de Rusia contra Ucrania […] [y] la participación de Bielorrusia».

Nota técnica
La norma de cadena de custodia PEFC considera la «madera de conflicto» como una «fuente conflictiva» (PEFC ST 2002:2020, 3.7), que no puede utilizarse en grupos de productos certificados PEFC (PEFC ST 2002:2020 Apéndice 1, 6.1). La «madera de conflicto» se define como «la madera que ha sido comercializada en algún momento de la cadena de custodia por grupos armados, ya sean facciones rebeldes o soldados regulares, o por una administración civil que participa en conflictos armados o sus representantes, bien para perpetuar el conflicto o para aprovecharse del mismo con fines lucrativos. (PEFC ST 2002:2020, 3.6).
La aclaración de que la madera de Rusia y Bielorrusia debe clasificarse como «madera de conflicto » se basa en la Resolución A/ES-11/L.1 de la Asamblea General de las Naciones Unidas (2 de marzo de 2022) «Agresión contra Ucrania» durante la 11ª Sesión Especial de Emergencia, y pretende salvaguardar la integridad de la certificación de la cadena de custodia PEFC. Esta aclaración es inicialmente válida por seis meses.
La entidad ha señalado que publicará nuevas directrices en los próximos días.
Información editada por Ricardo Saiz
Para más información contacte con AIDIMME.
Visitas: [wpstatistics stat=pagevisits time=total id=26971]
La empresa valenciana de logística de contenedores Docks participa en la herramienta Insylay
La empresa Docks se ha inscrito en la herramienta INSYLAY, plataforma de diagnóstico y asesoramiento para la implantación de modelos de cooperación sostenible entre empresas industriales, orientada a la obtención de una producción más eficiente y de menor impacto ambiental, mediante la aplicación de una metodología basada en el concepto de simbiosis industrial.
Entre el abanico de servicios ofrecidos por INSYLAY, se encuentra el guiado hacia la implantación y mantenimiento de Sistemas de Gestión de Calidad, Medio Ambiente.
Docks ha obtenido recientemente la certificación ISO 14001:2015 por su sistema de gestión ambiental, tras la auditoría realizada por la entidad Bureau Veritas para su depósito de reparación de contenedores marítimos situado en Riba-roja del Turia (Valencia).
Esta certificación deja patente el compromiso de Docks por utilizar de forma sostenible los recursos naturales y hacer un uso eficiente de la energía en sus instalaciones, optimizando el empleo de materias primas y fomentando las prácticas de reducción, reutilización y reciclado de los residuos generados, “respondiendo así a nuestras empresas clientes y resto de partes interesadas con la confianza absoluta de que Docks agregará valor y les apoyará en sus propias políticas ambientales”, explica la empresa.
Para lograr el éxito en este proceso de implantación del sistema de gestión ambiental, se ha implicado todo el equipo al que se le ha dado formación, fomentando su compromiso de respeto con el medio ambiente.
Además, este reconocimiento complementa otros hitos que la compañía valenciana ha obtenido como la certificación de la huella de carbono ISO 14064.

En esta línea de mejora continua, Docks está emprendiendo múltiples iniciativas desde diferentes ámbitos que contribuyen directa e indirectamente a la consecución de los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible (ODS), como la participación en proyectos como “INSYLAY” (plataforma de Economía Circular del Instituto Tecnológico AIDIMME), buscando el concepto de simbiosis industrial en la Comunidad Valenciana, a través de alianzas con otras organizaciones para el aprovechamiento de recursos subutilizados, tales como energía, agua, logística, capacidad, experiencia, equipos y materiales.
Puede leer la noticia completa en el siguiente enlace.

INSYLAY 3 INDUSTRIAL SYMBIOSIS LAYER AT INDUSTRIAL ZONES | Número de proyecto: 21900037 Expediente: IMDEEA/2019/70 Duración: Del 01/06/2019 al 30/06/2020 Coordinado en AIDIMME por: JORDA FERRANDO,LUCIA Línea de I+D: ECONOMÍA CIRCULAR |
Para más información contacte con AIDIMME.
Visitas: [wpstatistics stat=pagevisits time=total id=26919]
AIDIMME en el V Foro de Ingeniería y Sociedad. Ingeniería para el desarrollo sostenible
AIDIMME lleva más de veinte años apoyando a las empresas en el análisis y minimización de los impactos ambientales de sus actividades, así como desarrollando proyectos de I+D+i en materia de Sostenibilidad.
En este sentido, Alicia Pérez Torres, Jefa del Departamento de Gestión de Procesos y Sostenibilidad de AIDIMME, participó el pasado 4 de Marzo, con motivo del Día Mundial de la Ingeniería para el Desarrollo Sostenible de Naciones Unidas, en el V FORO INGENIERÍA Y SOCIEDAD. INGENIERÍA PARA EL DESARROLLO SOSTENIBLE, organizado por la Mesa de la Ingeniería Valenciana.
En su intervención, Alicia Pérez, Jefa de Sección de Gestión de Procesos y Sostenibilidad en AIDIMME, introdujo el concepto de Simbiosis Industrial y dio a conocer las herramientas y recursos que AIDIMME pone a disposición de las empresas industriales en dicha materia.
Alicia ha señalado que con los años se ha aprendido a prevenir la contaminación en lugar de actuar una vez el daño estaba hecho. “Hemos incluido en la conversación el tema de la coeficiencia, incorporando así, a la ecuación la parte económica. Las empresas van implantando la economía circular pero es un proceso lento y en el que nosotros les ayudamos con nuestras herramientas a la implantación de estas pautas y procesos sostenibles” ha explicado Alicia Pérez.
La simbiosis industrial
La simbiosis industrial es una de las principales herramientas de la economía circular que trata de reintroducir en los procesos industriales los recursos subutilizados de diferentes empresas, con el fin de mantenerlos en uso productivo durante más tiempo.
Para poder llevar a la práctica este concepto, AIDIMME ha desarrollado y pone a disposición de las empresas de la Comunidad Valenciana la plataforma “simbiosisindustrial.aidimme.es”, que facilita el establecimiento de sinergias entre ellas.
Si quiere conocer el programa completo del evento y desea formalizar su inscripción pulse en este enlace.
Más información, contacte con AIDIMME
Dra. María Alicia Pérez Torres
TECNOLOGÍAS Y PROCESOS
Gestión de Procesos y Sostenibilidad
Jefa Sección
Visitas: [wpstatistics stat=pagevisits time=total id=26726]
“Hay que reconocer la valía del I+D+i”
El último número del periódico «El Sector» -editado por la Federación Empresarial de la Madera y Mueble de la Comunidad Valenciana, Fevama, desde 1992-, publica una entrevista realizada por la periodista Ana Valdés al presidente de AIDIMME y Redit, Fernando Saludes. Pueden acceder al pdf del medio para ver el relato completo en su formato impreso.
«Preside la Red de Institutos Tecnológicos de la Comunidad Valenciana (Redit), el Instituto Tecnológico Metalmecánico, Mueble, Madera, Embalaje y Afines (Aidimme) y la Alianza de Tecnologías Innovadoras de la Comunidad Valenciana (Inndromeda). Esta dedicación le proporciona una visión intersectorial de la I+D+i que comparte con El Sector.»
(…)
Los institutos tecnológicos suponen un apoyo a las empresas en materia de I+D+i. Esa i minúscula no acaba de gustarle…
No somos plenamente conscientes como sociedad de la importancia de la innovación. Hemos tenido que recorrer un largo camino para reconocer la importancia de la ciencia, pero la innovación queda como una cuestión menor, y la propia i minúscula lo refleja. Desde los centros tecnológicos, reivindicamos la I mayúscula porque entendemos la Investigación, el Desarrollo y la Innovación como tres elementos fundamentales, complementarios y que se necesitan mutuamente. Y hay que reconocer la valía de todas ellas.

(…)
¿Está el futuro de las empresas en la innovación?
Siempre lo ha estado. Quizá ahora tengamos más consciencia de ello. En el entorno en el que nos movemos, globalizado y muy acelerado, se convierte en una premisa más que necesaria. Determinadas actitudes más relajadas o reactivas que antes el mercado te permitía, ahora el resultado es que te expulsa o te deja en la irrelevancia.
(…)
Y en madera y mueble, ¿cómo vamos en innovación?
En madera y mueble somos punteros. La Unidad de Madera y Mueble de Aidimme es referente nacional e internacional. Estamos liderando áreas como la economía circular, donde incluso coordinamos el Comité Estratégico en Economía Circular de la Agencia Valenciana de Innovación (AVI) y trabajamos en proyectos muy potentes en Europa y en España. Somos centro de excelencia en fabricación aditiva a nivel nacional. Somos referentes en ecodiseño, con los nuevos materiales y el renacer de la madera como material extraordinario en propiedades, prestaciones y circularidad. Apoyamos y acompañamos al sector en su digitalización, con el desarrollo de la industria 4.0. Y ofrecemos un gran soporte con el Observatorio Tecnológico de Mercado.
Acceso a la entrevista completa
Editado por Ricardo Saiz
Para más información contacte con AIDIMME.
Visitas: [wpstatistics stat=pagevisits time=total id=26894]